Your heart rate is a powerful indicator of your cardiovascular health and overall fitness. Monitoring and understanding your heart rate can provide valuable insights into your body’s functioning and help you optimize your workouts and daily activities. Let’s dive into the significance of heart rate, how to measure it, its connection to fitness levels, and tips for maintaining a healthy heart rate.
What is heart rate and why does it matter
Heart rate refers to the number of times your heart beats per minute (bpm). It serves as a fundamental measure of your cardiovascular system’s efficiency and can vary based on factors such as age, physical activity, stress, and health conditions. A healthy heart rate ensures an adequate supply of oxygen-rich blood to all parts of your body, supporting optimal organ function and overall well-being.
Measuring your heart rate
There are several ways to measure heart rate, with the two most common methods being taking your pulse manually and using a heart rate monitor. Taking your pulse involves placing two fingers (usually the index and middle finger) on your wrist or neck to feel your pulse and counting the beats for 15 seconds, then multiplying by 4 to get your bpm. Heart rate monitors, available as wearable devices or smartphone apps, offer real-time heart rate tracking during exercise and daily activities, providing more accurate and convenient measurements.
Heart rate zones and fitness levels
Understanding heart rate zones is crucial for tailoring workouts to achieve specific fitness goals. These zones are based on different percentages of your maximum heart rate (MHR), which is calculated as 220 minus your age. The zones are as follows:
- Resting zone: 50-60% of MHR – This is the heart rate when you are at complete rest.
- Fat-burning zone: 60-70% of MHR – In this zone, you burn a higher percentage of calories from fat during exercise.
- Cardio zone: 70-80% of MHR – This zone improves cardiovascular endurance and aerobic capacity.
- Threshold zone: 80-90% of MHR – Training in this zone helps increase lactate threshold and performance.
- Maximum effort zone: 90-100% of MHR – This zone pushes your limits and is suitable for high-intensity workouts.
Maintaining a healthy heart rate
A healthy heart rate, also known as a resting heart rate, is the number of times your heart beats per minute when you are at rest. It is an essential indicator of cardiovascular health and overall fitness. The normal resting heart rate for adults typically ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute (bpm), although well-trained athletes may have lower resting heart rates due to their increased cardiovascular efficiency.
A lower resting heart rate is generally associated with better cardiovascular fitness and heart health. Regular exercise, particularly aerobic activities like running, cycling, or swimming, can improve heart function, leading to a lower resting heart rate. Additionally, factors such as age, gender, fitness level, and overall health can influence resting heart rate.
Monitoring your resting heart rate can provide valuable insights into your cardiovascular health. If your resting heart rate is consistently above the normal range, it may indicate various health concerns, such as dehydration, stress, lack of physical activity, or certain medical conditions like anemia or thyroid disorders. In contrast, a resting heart rate significantly below the normal range may also be a cause for concern and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, getting adequate sleep, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption are some lifestyle factors that can contribute to a healthy heart rate and overall cardiovascular health. If you have concerns about your heart rate or cardiovascular health, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation, guidance, and appropriate recommendations.
In conclusion, a healthy heart rate is an essential aspect of cardiovascular well-being. By leading a healthy lifestyle and taking care of your heart, you can achieve a lower resting heart rate and improve your overall heart health. Monitoring and maintaining a healthy heart rate can positively impact your quality of life and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Do these things to create a healthy heart rate
Regular cardiovascular exercise: Engage in aerobic activities like running, cycling, swimming, or brisk walking to keep your heart strong and healthy.
Strength training: Building muscle mass through resistance training can improve heart health and overall metabolism.
Stress management: Chronic stress can elevate heart rate and contribute to various health issues. Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to manage stress levels.
Balanced diet: A nutritious diet low in saturated fats, sodium, and processed sugars supports heart health and maintains a healthy weight.
Adequate sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to allow your heart to rest and repair.
Aerobic workouts: Participate in dance classes, aerobics, or other forms of continuous and rhythmic exercise to sustain an elevated heart rate.
Jumping and plyometrics: Activities like jumping jacks, burpees, and box jumps can quickly increase your heart rate.
Climbing stairs: Opt for stairs instead of elevators or escalators to get your heart rate up.
Dancing: Whether it’s in a fitness class or at home, dancing can be an enjoyable way to boost your heart rate.
Active sports: Engage in sports like tennis, basketball, soccer, or any activity that involves continuous movement and raises your heart rate.
Skipping rope: Jumping rope is an excellent cardiovascular exercise that can rapidly elevate your heart rate.
A healthy heart rate with Fit at Home
Maintaining a healthy heart rate is essential for overall cardiovascular health and fitness. Fit at Home offers various home workouts for the whole family that can help you achieve and maintain a healthy heart rate. Use Fit at Home to achieve your heart health goals.
Your NUMBER ONE fitness app available on:
Fit at Home provides a convenient and effective platform to maintain a healthy heart rate through a variety of cardio, interval training, and strength workouts. By consistently engaging in these exercises and tracking your heart rate during workouts, you can work towards improving your cardiovascular fitness, reducing the risk of heart disease, and enhancing your overall well-being. As with any exercise program, listen to your body, and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any underlying health conditions or concerns before starting a new fitness routine. With commitment and dedication, Fit at Home can be an excellent tool to support your journey to a healthier heart.
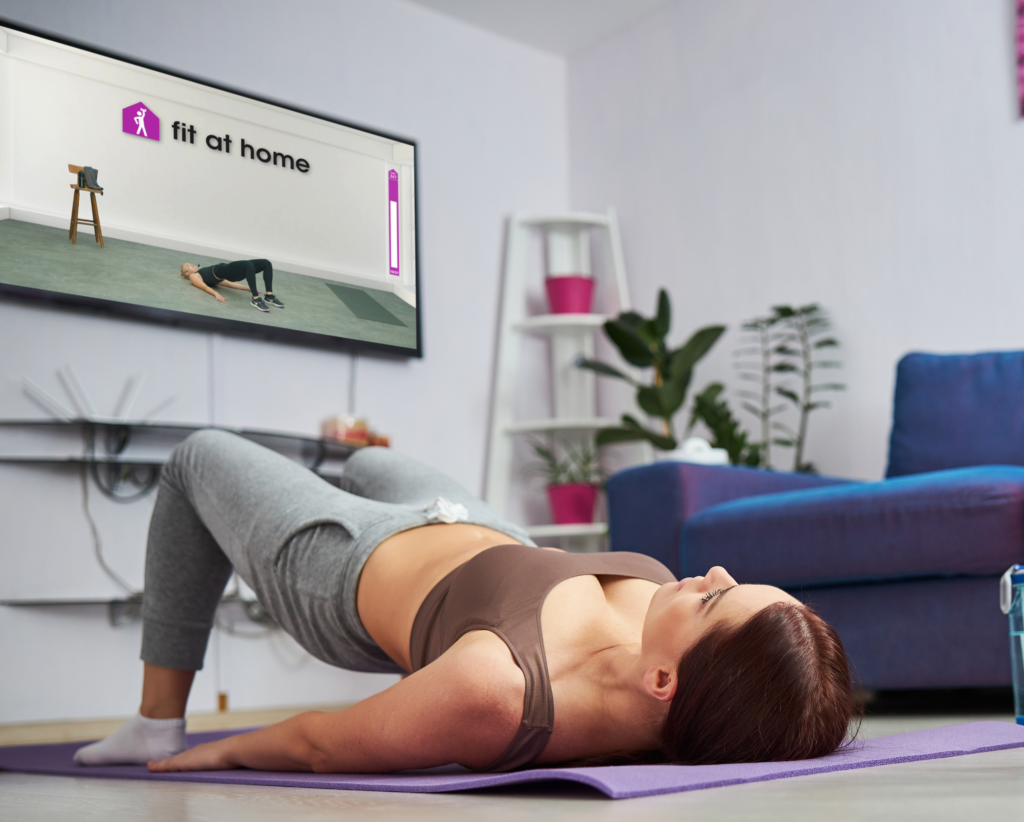

Transform your TV into your personal gym!
✓ Work out in front of your tv whenever you want
✓ 24/7 on-demand with more than 500 workouts
✓ For the whole family
Boosting your heart rate through regular physical activity is a cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle. It contributes to improved cardiovascular health, increased fitness levels, and a reduced risk of various health conditions. Incorporate aerobic exercises, strength training, and other forms of physical activity into your routine to enjoy these significant health benefits. Remember to start gradually if you’re new to exercise and always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your physical activity level, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Cardiovascular system
The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system, is a complex network of organs and blood vessels responsible for transporting blood, oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body. It plays a vital role in maintaining the body’s internal balance and supporting various physiological functions. Here’s an overview of the key components and functions of the cardiovascular system:
Key components of the cardiovascular system:
- Heart: The heart is the central organ of the cardiovascular system. It is a muscular pump located in the chest cavity and is responsible for pumping blood to all parts of the body. The heart has four chambers: two atria (upper chambers) and two ventricles (lower chambers). The right side of the heart receives oxygen-depleted blood from the body and pumps it to the lungs for oxygenation, while the left side receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the rest of the body.
- Blood vessels: Blood vessels are a network of tubes that carry blood to and from the heart and various organs and tissues. There are three main types of blood vessels:
- Arteries: These carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the body’s organs and tissues.
- Veins: These transport oxygen-depleted blood from the body back to the heart.
- Capillaries: These are tiny, thin-walled vessels that connect arteries and veins and allow for the exchange of nutrients, gases, and waste products between the blood and body tissues.
- Blood: Blood is a fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the cardiovascular system. It is composed of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues, while white blood cells are essential components of the immune system, defending against infections and foreign invaders. Platelets play a critical role in blood clotting to prevent excessive bleeding, and plasma is the liquid part of blood that carries nutrients, hormones, and waste products.
Functions of the cardiovascular system:
- Transportation: The cardiovascular system transports oxygen from the lungs to body tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs for elimination. It also carries nutrients from the digestive system to cells and removes waste products generated by cellular metabolism.
- Thermoregulation: Blood flow and circulation help regulate body temperature, distributing heat throughout the body and maintaining optimal temperature levels.
- Immune response: The cardiovascular system, through the actions of white blood cells, plays a role in the body’s immune response, defending against infections and pathogens.
- Hormone distribution: The circulatory system distributes hormones produced by various glands to target organs and tissues, regulating various physiological processes and maintaining homeostasis.
- Fluid balance: Blood vessels and capillaries play a role in maintaining fluid balance by preventing excessive fluid leakage into surrounding tissues.
The cardiovascular system is essential for sustaining life and ensuring the proper functioning of the body’s organs and systems. Taking care of your cardiovascular health through regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and regular medical check-ups is crucial for overall well-being and longevity.